We’re looking for part-time help with the podcast and newsletter! Spend ~10 hrs/week editing shows and putting together enhanced transcripts starting at $35/hr. All you need is enthusiasm for our content—no prior audio experience required (we use this software called Descript which is easy to learn and a pleasure to use).
Respond to this email if you’re interested with a little background on yourself.
This edition is brought to you by Pelanor, the AI-powered FinOps startup letting companies make sense of their cloud spend.
Founded by alumni of Israel’s elite cyber intelligence unit, Pelanor untangles the chaos behind nine-figure AWS and Azure bills. Most companies have no idea how their compute spend ties into business outcomes. That’s because the people managing infrastructure and the people using it rarely talk, let alone share ownership.
Pelanor solves this by building a dynamic graph of your cloud environment—tracking which microservices talk to which databases and how AI workloads are actually being used. Even non-technical team members can ask complex questions in plain English and get straight answers:
“What’s driving our OpenAI bill?”
“Which services are talking to unused databases?”
“Where can we save?”
Reach out to founder Matan Mates on LinkedIn or email him directly at matan@pelanor.io.
As Meta aggressively consolidated the US market for augmented reality glasses, it scared off what could have been a competitive AR ecosystem in the West. Only now with Google’s recent AR announcements at I/O is a second serious player back in the game. In the words of Leap Motion and Midjourney founder David Holz:
“VR and AR really needed 12 companies basically making products… [I]n two generations of 12 companies, we would have been way closer to something that was really compelling for everyone. But instead, we got one product, maybe two.”
In China, however, there has been no such consolidation, and a “Hundred Lens War” (百镜大战) has instead produced a vibrant AR ecosystem where small startups, rather than tech giants, lead. But does it matter that there are no American analogues to China’s “Five Little Dragons” of augmented reality (AR眼镜五小龙)?
Skepticism toward AR glasses is understandable (especially after the highly publicized failure of Google Glass), but the premature consolidation of the US market could have dramatic consequences one day. Real-time translation via a wearable product could be game-changing in linguistically diverse places like India; some consumers could be compelled by the prospect of using AR glasses as a real-time conversation guide; and maybe hyper-immersive Wii sports will prove to be even more fun than the low-tech version we enjoy today. The point is, we can’t really sit here in 2025 and say with certainty that AR glasses won’t have any compelling use cases.
If manufacturers eventually overcome technical challenges and get the public on board, AR glasses could generate tons of real-world audio and video data valuable for training AI, much like humanoid robots. This route to profitability could help buoy AR investment, even if the public isn’t sold on AR products yet. That could also partly explain why Xi tried on some AR glasses during his recent tour of Shanghai’s AI ecosystem.

Today’s article will explore China’s market for AR glasses and introduce China’s Five Little AR Dragons. It will also include my personal review of a Chinese-made AR headset that I was able to try in Taipei.
Terminology and the State of the Art
Augmented reality (AR) is distinct from virtual reality (VR) — AR headsets are designed to overlay digital features onto the user’s interaction with the real world, and can theoretically be worn for extended periods. VR products are designed for shorter periods of fully immersive use (Apple’s Vision Pro, for example, does both VR and passthrough AR). The umbrella term for both AR and VR is extended reality, or XR for short.
Chinese XR glasses manufacturers rely on microdisplays, primarily micro-LED and micro-OLED displays. While traditional OLED displays use a backplane made of glass, the pixels of micro-OLED displays are etched directly onto a silicon wafer (hence their alternative name, OLED on Silicon, or OLEDoS). Thanks to supply chains created for the Apple Vision Pro, the cost of producing these displays has dropped rapidly in China since 2023. In March, Chinese LEDoS manufacturer JBD cinched a deal with Meta to become the exclusive supplier of LEDoS displays for Meta’s Orion prototype.
Another key component is the waveguide. A waveguide is a transparent optical component that guides light from the display to the user’s eyes while allowing them to see the real world. The waveguide makes it possible to overlay digital content onto physical environments. As is the case with microdisplays, China’s leading suppliers of waveguides are based in Shanghai.
Five Little Dragons
What can these glasses do today? Traditionally, the industry has emphasized entertainment features (e.g., gaming, streaming movies and music, and shooting photos and videos) while touting the potential future benefits in education, medical care, and delivery logistics.
But after Meta announced new AI features for their Ray-Ban smart glasses in April 2024, China’s AR companies have been eager to capitalize on the “AI+AR” hype. According to Li Hongwei 李宏伟, CEO of the AR dragon RayNeo:
“Smartphones do not have the display features or capabilities of spatial perception interaction that AR glasses have. AI+AR glasses encompass three categories: mobile phone applications, AI smart assistants, and virtual reality integration. The latter two are opportunities for disruptive innovation. For this reason, more than half of the successful companies in the future AR market may not be traditional giants, but emerging companies.”
Still, less than 20% of designs in the Chinese smart glasses market had AI functions by the end of 2024. AI integration is difficult in part due to dependence on external computing power — suitable processors are simply way too big and energy-hungry to fit into the frames of the glasses. That’s why AR glasses often rely on split compute to preserve battery life — tasks like translation are offloaded to the user’s cellphone, and then the result is transferred to the glasses through WiFi to save power. This also means that AR companies benefit substantially from locking down partnerships with phone companies that control the ecosystem.
China's VR/AR industry reportedly raised 2.948 billion RMB (~US$340 million) across 30 investment and financing events from January to November 2024. While tech giants like Huawei and Xiaomi have been dabbling in AR, innovation has primarily been driven by the so-called “Five Little Dragons” of the AR industry: XREAL (优奈柯恩), RayNeo (雷鸟创新), Rokid (灵伴科技), INMO (影目科技), and the Xi-endorsed Meizu (星纪魅族).
Thanks to fierce domestic competition, most models of AR glasses currently available in China are in the price range of 2,000-4,000 RMB (~US$275-$550). By comparison, Meta’s Ray Ban glasses, which don’t include displays in the lenses, start at US$299, and their full-service Orion prototypes cost US$10,000 per unit to produce.
We’ll briefly highlight each company’s quirks below.
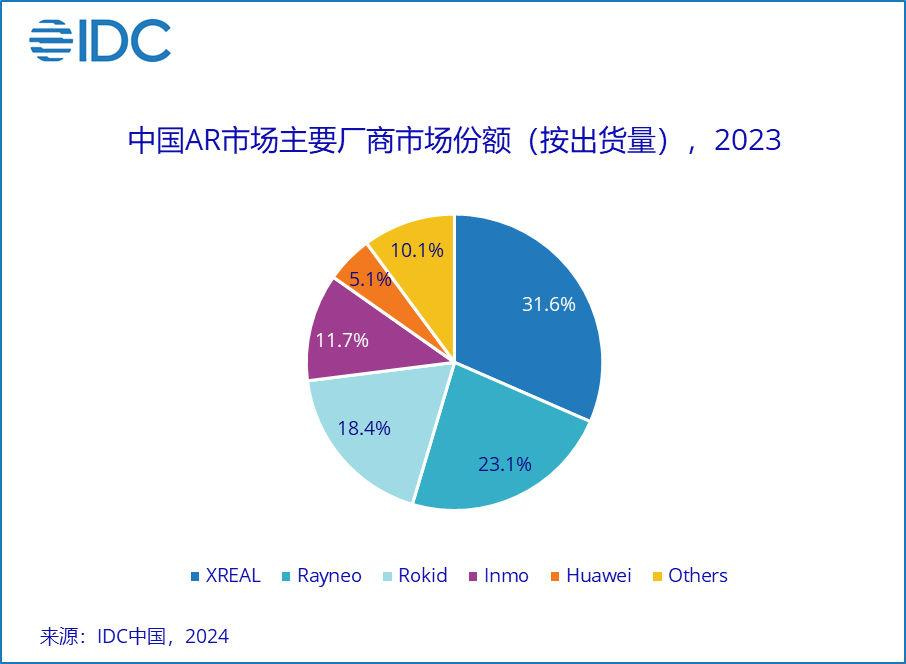
XREAL 优奈柯恩
XREAL was founded in Hangzhou by Xu Chi 徐驰, but the company has recently relocated its headquarters to Shanghai. While other AR startups primarily use Snapdragon processors made by Qualcomm, XREAL uniquely uses self-developed chips. XREAL’s X1 processors can reportedly achieve a latency of 3 milliseconds (compared to 12 milliseconds for the Apple Vision Pro). Xu explains:
“The X1 chip equipped in the XREAL One not only successfully resolves technical challenges like 3DoF spatial anchoring and ultra-low latency, but also fundamentally overcomes the longstanding issue of inconsistent cross-device experiences for AR glasses. In the past, to provide a consistent experience across different operating systems, we had to develop separate software for Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS platforms. Yet even then, it was difficult to fully ensure uniformity in the user experience. With XREAL One, however, we’ve finally found a more elegant solution. By integrating computing power directly into the glasses themselves, we’ve fundamentally changed the game — delivering a truly meaningful “AR for all” experience.”
Xu also noted that 65% of XREAL’s smart glasses components are developed and manufactured in-house, and the company is aiming for 100% hardware independence within the next two years. But this hardware-focused approach has tradeoffs — XREAL’s products don’t currently come equipped with out-of-the-box AI features, although the company claims that LLM integration will be included in a future software update. Here’s Xu’s justification for not engaging with the AI+AR hype:
“AR glasses are always centered around user experience. We won’t blindly build AI glasses just for the sake of having AI. Instead, we start from the user experience and work backwards to identify what kinds of technical innovation are necessary.
In the R&D process, we have to wisely understand the limits of current technology — knowing what’s realistically achievable and what isn’t, at least for now. Blindly chasing breakthroughs can lead to disastrous outcomes.
Although XREAL is a relatively small company, our strength lies in the smart use of limited resources. We’re very clear about where to allocate funds to keep our product logic sharp and focused.”
Consumer reviews of the XREAL glasses have been quite positive despite the lack of AR+AI branding. One reviewer from Hong Kong wrote in April of 2025:
These are the best AR smart glasses, perfect for entertainment whether you're out and about or relaxing at home (such as in a small apartment or lying in bed). Once connected to a compatible device via USB-C, users can watch their favorite shows, movies, or games on a large virtual screen, like having a private cinema.
The glasses feature a Full HD 120Hz OLED display with a brightness of up to 600 nits, delivering vivid images and excellent contrast for viewing dark scenes. The image quality is further enhanced by electrochromic dimming lenses, allowing users to adjust the lens brightness with a switch. At the clearest setting, the lenses let users easily see their surroundings, while at the darkest setting, they effectively block out external light, providing an almost perfect viewing experience.
In addition, the glasses boast impressive speakers, with sound quality tuned by Bose, offering rich audio across highs, mids, and lows. While using separate headphones can still enhance the audio experience, this is the first pair of smart glasses where users feel that headphones are an optional accessory rather than a necessity.
XREAL has also prioritized business partnerships under Xu, betting that the experience will translate to market share once AR technology is mature enough to garner widespread consumer interest. XREAL has inked deals with BMW, T-Mobile, AT&T, Bose, and Google.

RayNeo 雷鸟创新
RayNeo is a subsidiary of TCL, an electronics manufacturing giant that is partially state-owned. The company’s Mandarin name translates literally to “Thunderbird Innovations,” and they are notable for marketing AR products aggressively outside of China. CEO Li Hongwei 李宏伟 explains in an interview from January 2024:
“We wanted to establish a foothold in overseas markets first, so we started by working on distribution channels. For example, we launched on Amazon, and in November last year, we achieved strong results by ranking first on both the new arrivals chart and the bestsellers list in the smart glasses category.
Right now, we’re also selling our products in some boutique stores across Europe… and the sales performance there has been fairly good as well.”
RayNeo recently announced a partnership with the International Olympic Committee, so we’ll probably see promotional videos for Los Angeles 2028 shot from the perspective of athletes.
The company also partnered with Alibaba Cloud to develop a multimodal AI model specifically for AR glasses — now, the average response time for AI queries on RayNeo glasses is reportedly 1.3 seconds.
Finally, RayNeo was the first company in the Chinese market to sell AR glasses for less than 2,000 RMB. Here’s how they keep costs low, according to Li:
“If Meta’s Orion is the Vision Pro of AR glasses, then the RayNeo X3 Pro is more like the “Vision.” …It does not use the most cutting-edge technology in all technical indicators like Orion…. For example, in the selection of optical waveguides, although RayNeo has a silicon carbide wafer version internally, our commercial products do not use this material. Instead… we use photolithography machines and chip etching processes to make waveguides on glass, so as to better balance costs and product experience. As the company's strategy, RayNeo will not choose to pile up all the industry's most advanced technologies in listed products for the sake of showing off its skills, but will develop cutting-edge technologies and products internally, and eventually launch leading, pragmatic, and mass-producible products to the market.”

Rokid 灵伴科技
Rokid was founded in Hangzhou in 2014 by Zhu Mingming 祝铭明, who left his job at Alibaba to start the company. In 2024, Rokid received nearly 500 million RMB and 100 million RMB across two rounds of financing. Their AI-equipped glasses use Alibaba’s Qwen models for real-time translation.
Among the AR dragons, a uniquely large portion of Rokid’s investors are SOEs. Here’s Zhu’s explanation from an April 2025 interview:
We have significant influence on the B2B side — the cultural and museum market alone is worth around a hundred million yuan annually. Our ecosystem partners bring in tens of millions, and each year, several million people visit museums. Rokid is the only player in this sector. …
B2B operations serve as a bridge for interacting with the government. Even in local governments with no overlapping business opportunities, there are always departments for cultural tourism and museums.
Rokid partnered with the PLA to build custom AR glasses for use on China’s space station. Their website also highlights B2B partnerships with oil, gas, and mining operations. But for now, Rokid’s consumer products receive mixed reviews.
I was able to try the Rokid Max AR glasses at the Guanghua Digital Plaza in Taipei. I watched a clip from Avengers: Endgame with the glasses, and the image quality was quite nice. You can correct for nearsightedness without customized lenses if your prescription is between 0.00D and -6.00D. I expected my eyes to feel strange switching between far-away objects and the close-up digital projection (as is reported by many reviewers), but I didn’t notice any such feeling during short-term use.
Unfortunately, they are very ugly and sit weirdly far and high up on your face. They’re also not wireless (unless you buy a wireless adapter, which adds latency), and the Rokid Max glasses I tried don’t support AI features like translation (Rokid’s AI-equipped glasses are a separate product line).

My impression is that, for now, the most tangible use case for these glasses is avoiding neck strain.
INMO 影目科技
INMO’s Chinese name could be translated as “Image Eye Technologies.” As a newer entrant into the Chinese AR market, their strategy has focused on affordable consumer AR with basic features, advertising use cases like cycling directions, translation, and taking notes in meetings. The company marketed their INMO GO glasses as “the first consumer-grade AR glasses with deep AI integration,” highlighting translation capabilities in 11 languages, smart notifications, and AI assistant features supported by ChatGPT. Here’s INMO founder and CEO Yang Longsheng 杨龙昇 on his vision for popularizing AR glasses:
“We hope that AI glasses can be like a personal assistant in the future, helping me order takeout, order a cup of coffee, etc. at any time. …
In the past, social interaction was generally between real people, but based on the emergence of AI and the improvement of technologies such as virtual humans, I believe that in the near future, perhaps within four or five years, people will be able to socialize with these virtual intelligent entities.
I can create a virtual image of my dreams, infuse it with the personality I want, and then interact with it in this entire virtual-real world. …
[AI companies] also need to find some landing points for these intelligent entities. Glasses are undoubtedly the best form at present, which also encourages them to try more content on glasses.”
INMO’s content partners include Baidu (China’s Google analogue), TanTan (a dating app), and game developers NetEase and 37Games. Chinese reviewers seem to appreciate the INMO software ecosystem — one user wrote,
“The INMO AIR 3 uses the IMOS 3.0 operating system, an OS specifically designed for AI+AR terminals. The AIR 3 can project the equivalent of a 150-inch giant screen. With the help of a 3DoF smart ring, the AIR 3 supports screen-space hovering functionality. IMOS 3.0 provides more efficient applications and a more immersive experience through intelligent interaction and spatial display capabilities. IMOS 3.0 not only supports native AR applications but is also compatible with most Android apps on the market, offering a relatively rich content ecosystem.”
INMO also recently announced a partnership with China Mobile to integrate their AR products with China Mobile’s Jiutian LLM ecosystem.

Meizu 星纪魅族
Meizu is owned by Geely, a conglomerate that primarily manufactures automobiles and holds a controlling stake in Volvo. Meizu’s primary business ventures are smartphone manufacturing and developing the FlyMe Auto operating system used by many Geely-owned car brands. As such, Meizu’s AR glasses are compatible with FlyMe-equipped vehicles.
At the 2025 Shanghai Global Investment Promotion Conference, Meizu founder Li Shufu 李书福gave a highly-publicized speech while wearing a pair of Meizu glasses, which acted as a teleprompter.
The company has developed its own FlyMe LLM, but Meizu glasses also support integration with third-party AI models, including DeepSeek, Qwen, and ByteDance’s Doubao. In early 2024, the company signed a partnership with Malaysia's Juwei Group to expand sales of Meizu glasses in Southeast Asian markets.

Looking Forward
China’s “Hundred Lens War” is a live experiment in hardware innovation under pressure. While consumer interest remains tepid, China’s Five Little Dragons are constantly launching new products in search of the ideal combination of design choices — wired vs wireless, with lens displays vs without, AI vs traditional translation, and many more. If AR glasses eventually succeed in locking down compelling use cases, it’s likely just as likely their decisive breakthroughs will come from not from Silicon Valley but Shanghai.
Thanks to Mike G. and Benjamin Reinhardt for offering feedback on previous drafts of this article.






Great piece! China is really taking the in a number of tech sectors. I had no idea the amount of Chinese companies that existed in this space. Also, those Rokid Max AR glasses are definitely a bit funky looking.
Information overload leading to increase stress over overstimulation. This will end up affecting the immune defenses of bodies.
Evolutionary speaking, organisms have in fact developing filtering techniques to remove the "noise" and focus on the "signal" that reaches their decission centers.
Nice way to fuck with that. Or sabotaging the long term fitness in a population...